NORTHEAST INDIA ?
NORTHEAST INDIA ?
Northeast India (officially North Eastern Region, NER) is the easternmost region of India representing both a geographic and political administrative division of the country.
History
The earliest settlers may have been Austro-Asiatic speakers from Southeast Asia, followed by Tibeto-Burmese from China and by 500 B.C. Indo-Aryans speakers from Gangetic Plains. Due to the bio- and crop diversity of the region, archaeological researchers believe that early settlers of Northeast India had domesticated several important plants. Writers believe that the 100 BC writings of Chinese explorer, Zhang Qian indicate an early trade route via Northeast India. The Periplus of the Erythraean Sea mention a people called Sêsatai in the region, who produced malabathron, so prized in the old world.
In the early historical period (most of first millennium), Kamarupa straddled most of present-day Northeast India, besides Bhutan and Sylhet in Bangladesh. Xuanzang, a travelling Chinese Buddhist monk, visited Kamarupa in the 7th century. He described the people as "short in stature and black-looking", whose speech differed a little from mid-India and who were of simple but violent disposition. He wrote that the people in Kamarupa knew of Sichuan, which lay to the kingdom's east beyond a treacherous mountain. For many of the tribal peoples, their primary identification is with subtribes and villages, which have distinct dialects and cultures.
The northeastern states were established during the British Raj of the 19th and early 20th centuries, when they became relatively isolated from traditional trading partners such as Bhutan and Myanmar. Many of the peoples in present-day Mizoram, Meghalaya and Nagaland converted to Christianity under the influence of British (Welsh) missionaries.
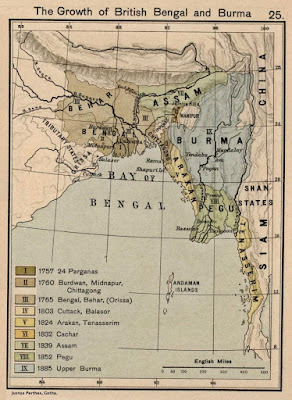
Formation of North Eastern states
In the early 19th century, both the Ahom and the Manipur kingdoms fell to a Burmese invasion. The ensuing First Anglo-Burmese War resulted in the entire region coming under British control. In the colonial period (1826–1947), North East India was made a part of Bengal Province from 1839 to 1873, when Assam became its own province.
After Indian Independence from British Rule in 1947, the Northeastern region of British Indiaconsisted of Assam and the princely states of Manipur and Tripura. Subsequently, Nagaland in 1963, Meghalaya in 1972, Arunachal Pradesh in 1975 (capital changed to Itanagar) (formed on 20 February 1987) and Mizoram in 1987 were formed out of the large territory of Assam. Manipur and Tripura remained as Union Territories of Indiabetween 1956 until 1972, when they attained fully-fledged statehood. Sikkim was integrated as the eighth North Eastern Council state in 2002.
The city of Shillong served as the capital of the Assam province created during British Rule. It remained as the capital of undivided Assam until formation of the state of Meghalaya in 1972.The capital of Assam was shifted to Dispur, a part of Guwahati, and Shillong was designated as the capital of Meghalaya.
Geography
The Northeast region can be physiographically categorised into the Eastern Himalaya, the Patkai and the Brahmaputra and the Barak valley plains. Northeast India (at the confluence of Indo-Malayan, Indo-Chinese, and Indian biogeographical realms) has a predominantly humid sub-tropical climate with hot, humid summers, severe monsoons, and mild winters. Along with the west coast of India, this region has some of the Indian sub-continent's last remaining rain forests, which support diverse flora and fauna and several crop species. Reserves of petroleum and natural gas in the region are estimated to constitute a fifth of India's total potential.
The region is covered by the mighty Brahmaputra-Barak river systems and their tributaries. Geographically, apart from the Brahmaputra, Barak and Imphal valleys and some flat lands in between the hills of Meghalaya and Tripura, the remaining two-thirds of the area is hilly terrain interspersed with valleys and plains; the altitude varies from almost sea-level to over 7,000 metres (23,000 ft) above MSL. The region's high rainfall, averaging around 10,000 millimetres (390 in) and above, creates problems of ecosystem, high seismic activity, and floods. The states of Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim have a montane climate with cold, snowy winters and mild summers.




Comments
Post a Comment